Intracranial plaque regression after intensive medical treatments: a high-resolution MRI observation
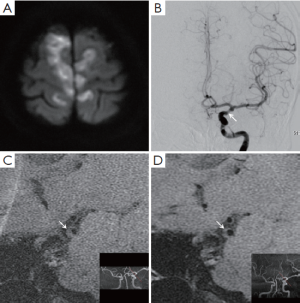
A 54-year-old female had bilateral infarcts in a parasagittal distribution (Figure 1A). Digital subtraction angiography showed a low-grade stenosis at the terminal segment of left internal carotid artery (ICA), with a plaque on high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (HR-MRI) (Figure 1B,C). Clopidogrel 75 mg/day, atorvastatin 60 mg/day, and amlodipine 5 mg/day were prescribed. Eighty days after the treatments, ICA plaque regression was observed on repeated HR-MRI (Figure 1D). There was no stroke recurrence. Our case suggests HR-MRI has made it possible to quantify intracranial plaque burden and evaluate its progression (1). Intensive medical treatments may play a role in reversing intracranial atherosclerosis, like they do in extracranial atherosclerosis (2).
Acknowledgements
Funding: Supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China (NCET-12-0069).
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu WH, Li ML, Gao S, et al. In vivo high-resolution MR imaging of symptomatic and asymptomatic middle cerebral artery atherosclerotic stenosis. Atherosclerosis 2010;212:507-11. [PubMed]
- Okazaki S, Yokoyama T, Miyauchi K, et al. Early statin treatment in patients with acute coronary syndrome: demonstration of the beneficial effect on atherosclerotic lesions by serial volumetric intravascular ultrasound analysis during half a year after coronary event: the ESTABLISH Study. Circulation 2004;110:1061-8. [PubMed]


